算术表达式语法分析
编译原理的第二次实验,使用 LR 方法实现对算术表达式的语法分析
DFA
首先要根据文法构建一个 DFA
构造拓广文法 G(s)
构造有效项目集和相应 DFA
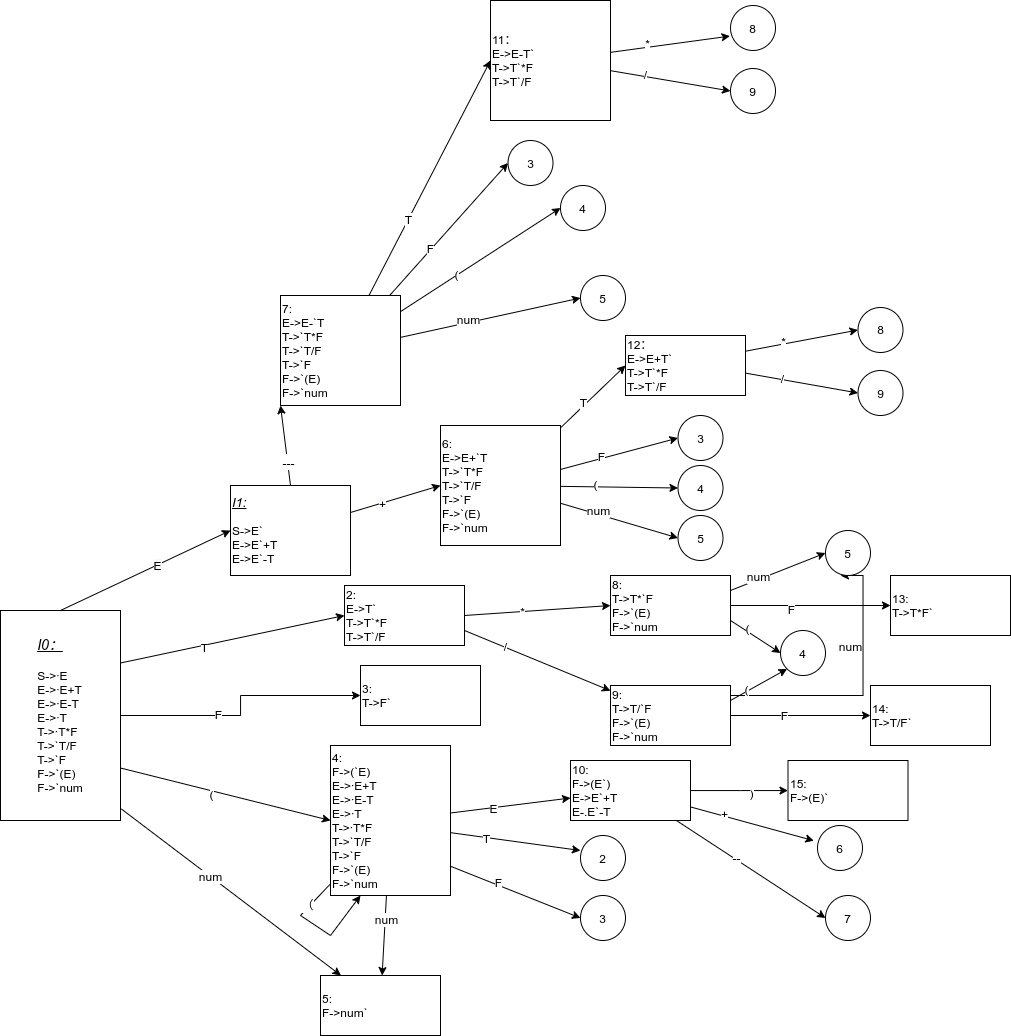
SLR
从 DFA 中可以观察到使用 LR(0)将会有 Shift-Reduce 冲突,所以最终使用 SLR 分析。
构造 SLR 需要在 LR(0)的基础上计算出 First 和 Follow 集合
构造 FIRST 和 FOLLOW 集合
| E | T | F | |
|---|---|---|---|
| First | (,num | (,num | (,num |
| Follow | +,-,#,) | +,-,#,*,/,) | +,-,#,*,/,) |
构造 SLR 分析表
规约时,需要判断下一个的符号是否属于被规约状态的 Follow 集合中。在 Follow 集合中才允许被规约
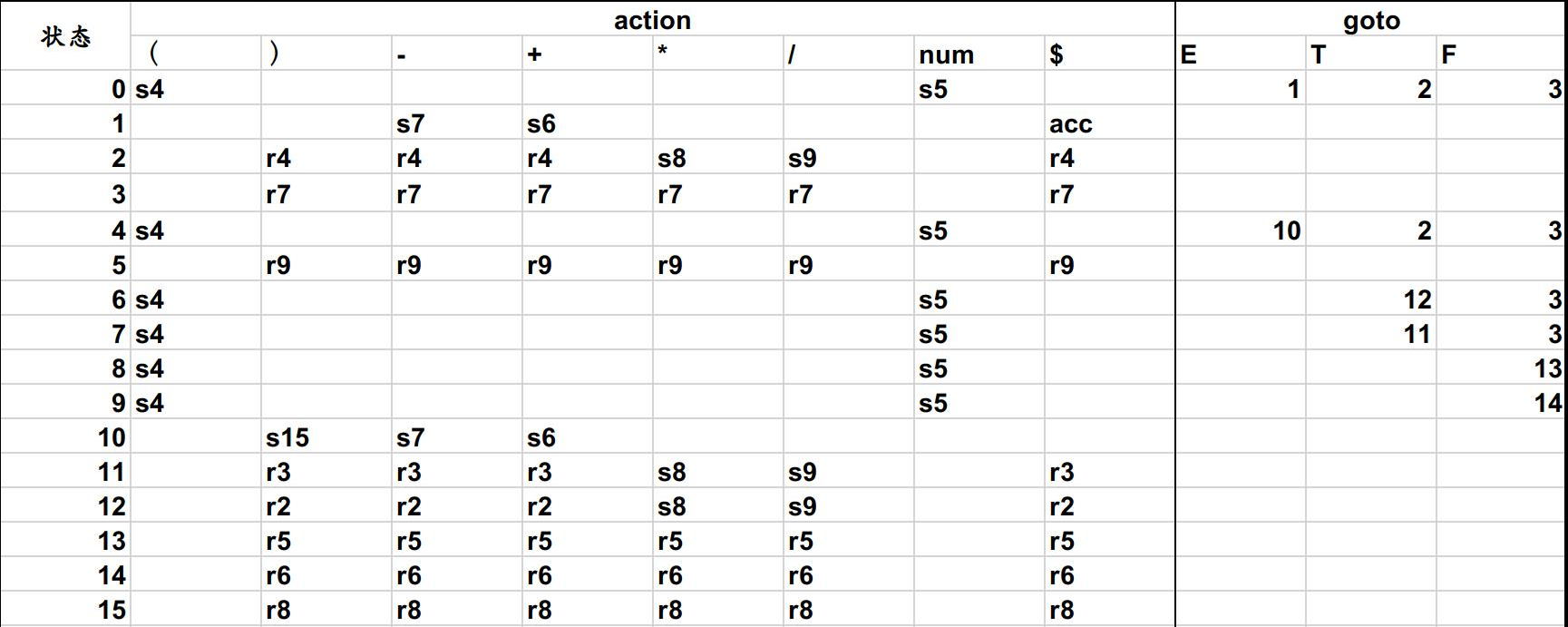
编写代码
相对于之前构造 DFA 和分析表,代码的实现显得则更为简单。但要注意代码的质量。
算法

实现
实现的关键在于:
-
Action,ActionKind
-
保存 ActionMap 和 GotoMap,产生式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58typedef unordered_map<string, Action> ActionMap;//需要16个,与状态数对应 typedef unordered_map<string, State> GotoMap;//需要16个,与状态数对应 const pair<string, string> producers[] = { {"T", "T*F"}, //... //将产生式填入 }; void initialMaps(vector<ActionMap> &am, vector<GotoMap> &gm) { const string actions[16][11]{ {"s4", "", "", "", "", "", "s5", ""}, {"", "", "s7", "s6", "", "", "", "a11"}, //... }; const int gotos[16][3] = { {1, 2, 3}, //... }; // ( ) - + * / num $ // E T F for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) { ActionMap a; GotoMap g; for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) { a[T[j]] = parse2Action(actions[i][j]); } for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) { g[V[k]] = gotos[i][k]; } am.push_back(a); gm.push_back(g); } } //从表中解析出Action // string s format:a char+digits,like s1,r2,a1 Action parse2Action(string s) { if (s.length() == 0 || s.length() > 3) { return Action{Error, Error}; } char kind = tolower(s[0]); int id = stoi(s.substr(1, s.length() - 1)); switch (kind) { case 'r':return Action{Reduce, id}; case 's':return Action{Shift, id}; case 'a':return Action{Accpet, Accpet}; default:return Action{Error, Error}; } } -
Lexer
由于是语法分析实验,所以词法分析写的比较简单
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17// simple lex,suppose that there is no error in token while lexing // // return like{"(","num",")"} vector<string> lex2Str(string sourceStr) { vector<string> ans; for (int i = 0; i < sourceStr.length(); i++) { string cur = string{sourceStr[i]}; if (T.find(cur) != T.end()) { ans.push_back(cur); } else { // parse num ans.push_back("num"); i += 2; } } return ans; } -
StatesStack,EnteredStack,CharacterQueue 三个关键数据结构的维护与 Parse 函数的编写
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65class DigitExpressionParser { private: stack<string> entered; queue<string> characters; unordered_set<string> T{"(", ")", "-", "+", "*", "/", "num", "$"}; unordered_set<string> V{"E", "T", "F"}; stack<State> states; vector<ActionMap> am; vector<GotoMap> gm; vector<string> lex2Str(string sourceStr) // function overload for different container to pop numofEle void pop(queue<string> &q, int num) void pop(stack<string> &s, int num) void pop(stack<State> &s, int num) // initial parser bool _init(string sourceString) public: DigitExpressionParser() { initialMaps(am, gm); } // parse bool parse(string sourseStr) { if (!_init(sourseStr)) { cerr << "Error:source string empty or wrong token" << endl; return false; } while (true) { State curState = states.top(); string curCharacter = characters.front(); auto &action = am[curState][curCharacter]; switch (action.kind) { case Shift:states.push(action.id); entered.push(curCharacter); characters.pop(); break; case Reduce: { // use producer[id] to reduce printProducer(action.id); auto producer = producers[action.id]; int popNum = producer.second == "num" ? 1 : producer.second.size(); pop(states, popNum); pop(entered, popNum); entered.push(producer.first); states.push(gm[states.top()][producer.first]); } break; case Error:cerr << "Error while parsing" << endl; return false; case Accpet:cout << "Accepted" << endl; return true; } } } };
优化
实验上有一些是可以优化(卷)的
- First 和 Follow 集合,有效项目集,分析表能够使用代码自动生成
- num 的可以使用数字代替,解析为 token
如果觉得不够卷还可以
- 可视化(呸)
- 写一个计算器